As concerns for the environment and climate change continue to grow, the architectural industry has responded with a shift towards sustainable design. Green architecture, also known as sustainable design, focuses on creating buildings that minimize environmental impact, reduce resource consumption, and prioritize occupant well-being. This article explores the principles and innovations of sustainable design and provides a glimpse into the future of green architecture.
- The Need for Sustainable Design: The urgency to address environmental challenges has led to a renewed focus on sustainable design in architecture. Buildings are responsible for a significant portion of energy consumption, carbon emissions, and resource depletion. Sustainable design aims to minimize these impacts by integrating environmentally friendly practices and technologies into the design, construction, and operation of buildings.
- Passive Design Strategies: Passive design strategies play a crucial role in sustainable architecture. These strategies maximize natural resources such as sunlight, wind, and shading to reduce the need for mechanical heating, cooling, and lighting. Design elements such as orientation, building shape, window placement, and insulation help optimize energy efficiency and create comfortable indoor environments.
- Energy-Efficient Systems: Advancements in technology have led to the development of highly efficient systems for heating, cooling, and lighting in buildings. Energy-efficient HVAC systems, LED lighting, and advanced controls help minimize energy consumption while maintaining occupant comfort. Integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal systems, further enhances the sustainability of buildings.
- Water Conservation and Management: Sustainable design emphasizes water conservation and management. Technologies like low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and graywater recycling allow for reduced water consumption in buildings. Designing landscapes with native plants and efficient irrigation systems also helps conserve water resources.
- Sustainable Materials: The selection of sustainable materials is essential in green architecture. Using locally sourced and renewable materials reduces the environmental impact associated with transportation and extraction. Recycled materials, such as reclaimed wood or recycled steel, are increasingly being used to minimize waste and promote a circular economy. Additionally, the use of non-toxic and low-emitting materials ensures a healthier indoor environment for occupants.
- Life Cycle Assessment: Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a valuable tool in sustainable design. LCA evaluates the environmental impacts of a building throughout its entire life cycle, from material extraction and construction to operation and end-of-life disposal. By considering factors such as energy consumption, carbon emissions, and waste generation, architects can make informed decisions to minimize the overall environmental footprint of a building.
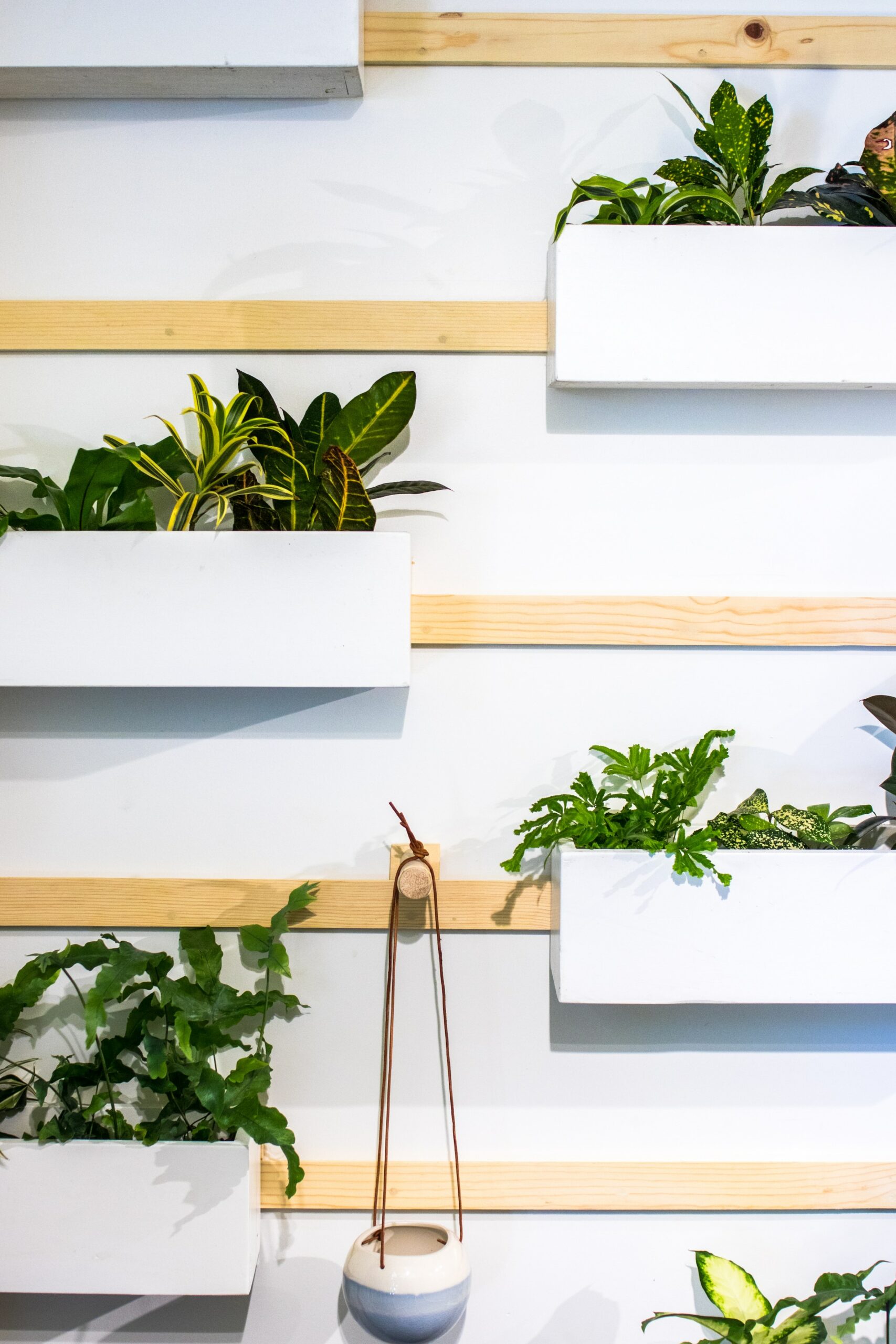
- Biophilic Design: Biophilic design incorporates elements of nature into the built environment, promoting health, well-being, and connection to the natural world. Integration of natural lighting, indoor plants, green walls, and outdoor spaces enhances the aesthetic appeal and improves indoor air quality. Biophilic design also supports productivity, creativity, and overall occupant satisfaction.
- Smart Building Technology: The future of sustainable architecture lies in the integration of smart building technology. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables buildings to collect and analyze data in real-time, optimizing energy usage, comfort, and maintenance. Smart sensors, automated controls, and building management systems allow for proactive energy management and efficient operation of buildings.
- Net-Zero Energy Buildings: Net-zero energy buildings (NZEBs) are an ambitious goal of sustainable design. These buildings generate as much energy as they consume over the course of a year. NZEBs combine energy-efficient design strategies, on-site renewable energy generation, and energy storage systems to achieve a net-zero energy balance. Advancements in solar power, energy storage technologies, and building automation systems will drive the future development of NZEBs.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Sustainable architecture extends beyond individual buildings to encompass sustainable urban planning. Designing cities that prioritize walkability, public transportation, green spaces, and mixed-use development reduces the need for excessive energy consumption and supports a sustainable lifestyle. Future sustainable cities will integrate renewable energy infrastructure, smart transportation systems, and resilient design principles to create thriving and environmentally conscious communities.
Sustainable design is not just a trend but a necessity for the future of architecture. Green architecture combines innovative design strategies, energy-efficient systems, sustainable materials, and smart technologies to create buildings that minimize environmental impact and prioritize occupant well-being. As the world continues to face environmental challenges, the adoption of sustainable design principles and the development of innovative solutions will pave the way for a greener and more sustainable built environment. By embracing sustainability, architects have the power to shape a future where buildings harmonize with nature and contribute to a healthier planet for generations to come.